Semantic Segmentation from Remote Sensor Data and the Exploitation of Latent Learning for Classification of Auxiliary Tasks, CVIU 2021
ICT researcher Bodhiswatta Chatterjee’s journal paper “Semantic Segmentation from Remote Sensor Data and the Exploitation of Latent Learning for Classification of Auxiliary Tasks” is published in Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2021. The paper is co-authored by Chatterjee B., Poullis C.
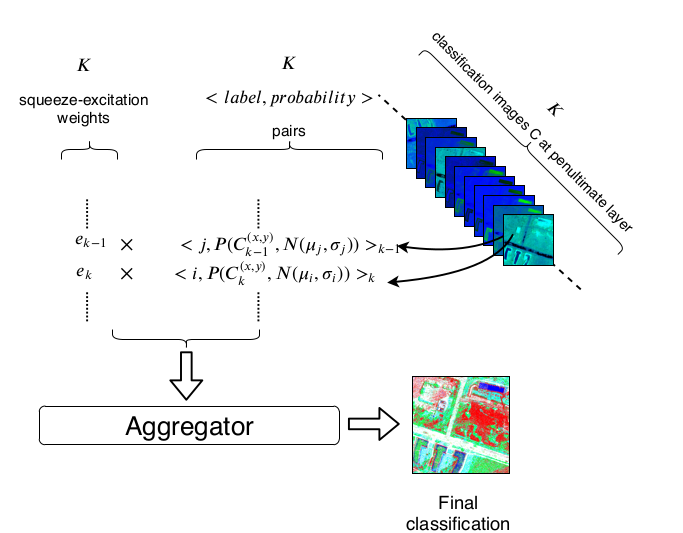
Abstract: In this paper, we address three different aspects of semantic segmentation from remote sensor data using deep neural networks. Firstly, we focus on the semantic segmentation of buildings from remote sensor data and propose ICT-Net: a novel network with the underlying architecture of a fully convolutional network, infused with feature re-calibrated Dense blocks at each layer. Secondly, as the building classification is typically the first step of the reconstruction process, we investigate the relationship of the classification accuracy to the reconstruction accuracy. Finally, we present the simple yet compelling concept of latent learning and the implications it carries within the context of deep learning. We posit that a network trained on a primary task (i.e. building classification) is unintentionally learning about auxiliary tasks (e.g. the classification of road, tree, etc) which are complementary to the primary task. We present the results of our experiments and explain how knowledge about auxiliary and complementary tasks – for which the network was never trained – can be retrieved and utilized for further classification. The source code and supplemental material are publicly available at https://theICTlab.org/assets/lp/2020ICTNet/
